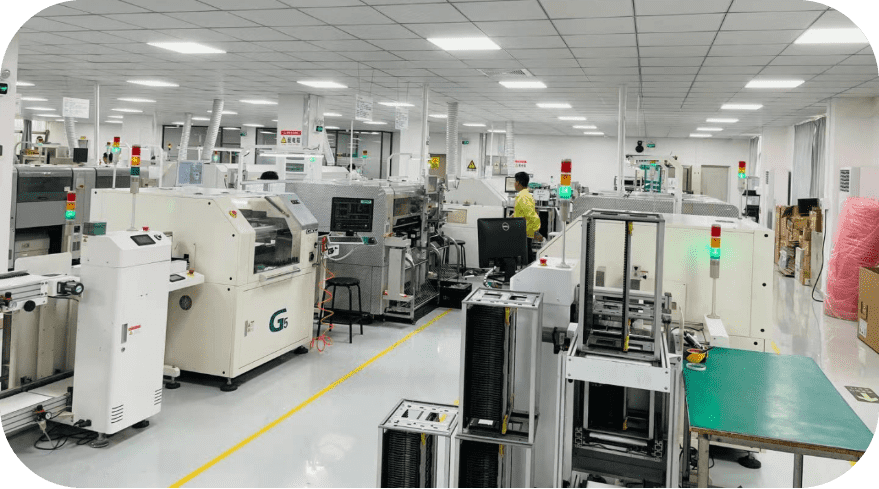
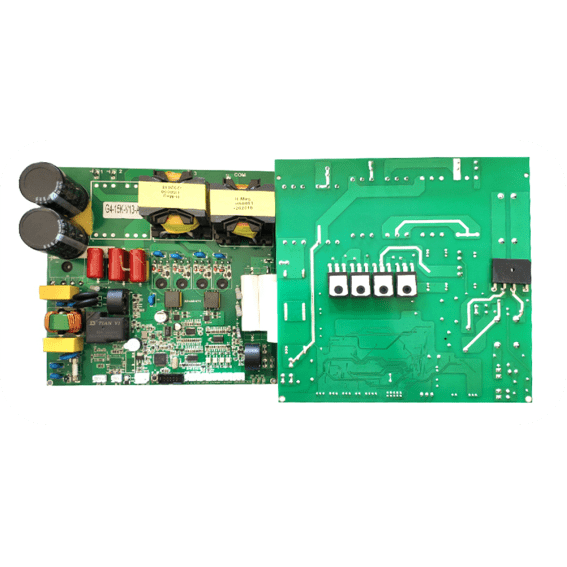
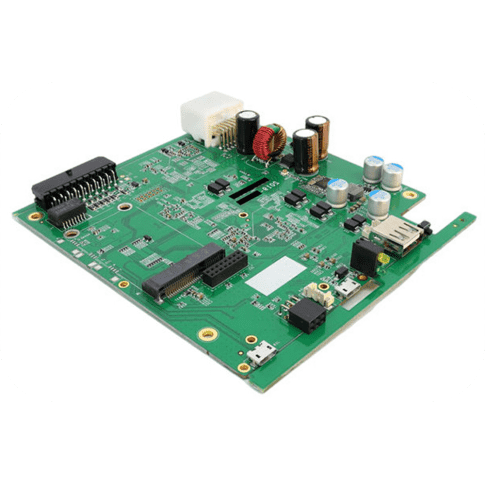
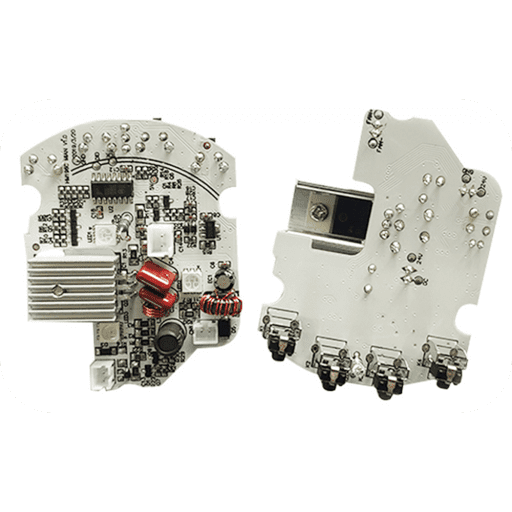
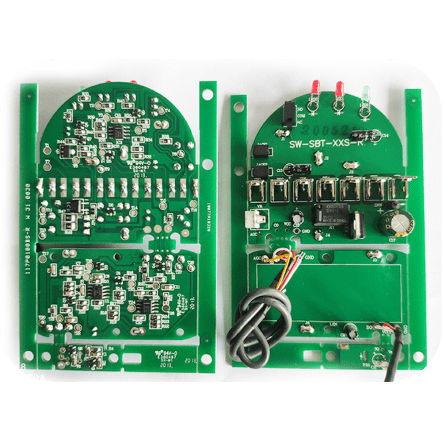
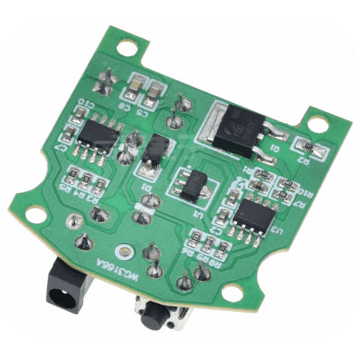
PCB Assembly, also known as Printed Circuit Board Assembly, refers to the process of assembling electronic components onto a printed circuit board. It involves various stages such as component placement, soldering, and testing to create a functional electronic device.
During the PCB assembly process, electronic components like resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), connectors, and other passive or active devices are mounted onto the designated positions on the circuit board. This is typically done using automated machines or manual labor depending on the complexity of the assembly.
The first step in PCB assembly is component placement. The components are carefully positioned and aligned with their corresponding pads on the circuit board. This can be done through pick-and-place machines that accurately position each component based on programmed instructions.
Once all components are placed correctly, soldering takes place to establish electrical connections between them and the circuit board. Solder paste is applied to each pad before reflow soldering or wave soldering techniques are used to melt it and form secure bonds between components and pads.
After soldering, thorough inspection and testing procedures ensure that there are no defects or faults in the assembled PCBs. Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems may be employed for visual inspections while functional tests verify if all components function properly according to specifications.
PCB assemblies find applications in various industries including consumer electronics, automotive electronics, telecommunications equipment manufacturing, medical devices production among others. They serve as vital building blocks for countless electronic products we use daily such as smartphones, computers, televisions etc.